
1.Preface
Steel is the most common material used in almost all products i.e., from households to industrial application. Significant part of the economy is steel sector based; however, steel has one large disadvantage – its high corrosion rate. Hence protection of steel structures and components assumes great economic importance. In tropical climes like the Indian subcontinent, the rate of corrosion is quite high considering hot and humid environmental conditions.

Shankar Sengupta Head – Energy Engineering Group, Adani Corporate House, Ahmedabad
Zinc is mostly used as an anti-corrosion agent and is being used from very early ages i.e., from 200BC to obtain brass which is an alloy of copper and zinc. It has inherent natural capacity to protect steel against corrosion.
In 1742, a chemist known as Melouin found that a zinc coating could be applied to iron by dipping it into molten zinc, laying the foundation for galvanizing. In 1780, an Italian physicist, Luigi Galvani, observed that the contact between two dissimilar metals resulted in the flow of an electrical current. His work led to the evolution of galvanization leading to the name of this physicist becoming synonymous with Galvanization. In 1836, a French civil engineer, inventor cum chemist, Stanislas Sorel patented a method of galvanization by cleaning steel and then dipping it into molten zinc. This was the beginning of modern hot-dip galvanizing.
2. Benefits of Galvanization
Hot-dip galvanizing has been in use over 100 years to protect steel corrosion worldwide; however, over time, many new material and process has been evolved. But hot-dipped galvanization remains the most trusted till date.
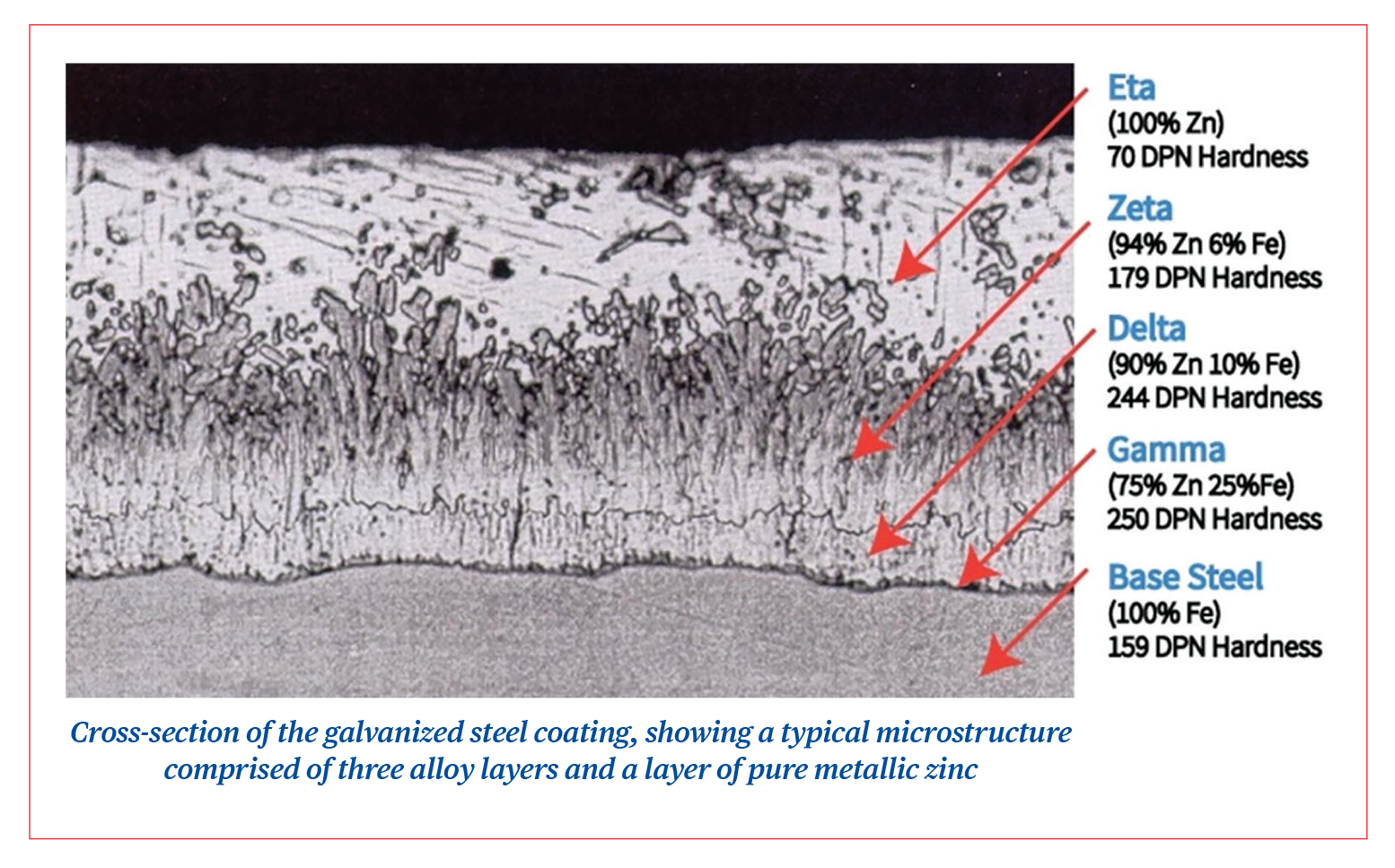
In the HDG process, the base material gets three-level protection.
i. Zinc layer barrier protection which protects steel by insulating direct contact with air and moisture.
ii. Cathodic protection wherein zinc acts as anode and sacrifices itself protecting the steel from corrosion
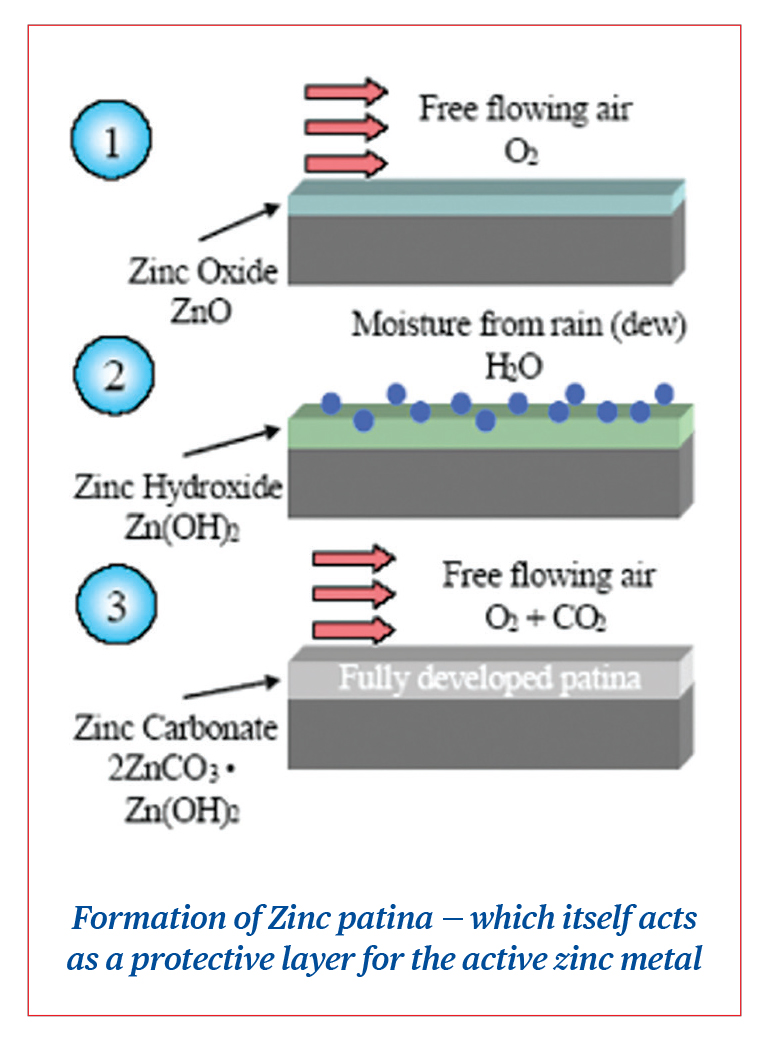
iii. Zinc Patine, wherein zinc oxidizes and builds a protective layer over steel.
3. Reasons for Opting for Hot -Dipped Galvanization Over Pre-Galvanization from Developers’ Perspective
 i. There may be various other ways of corrosion protection; however galvanized coating is one of the most durable forms of corrosion protection. In an ideal condition i.e., without any operation loads on the steel structure i.e., if the galvanized steel is kept, with average coating thickness of 85 microns, it will protect the base material for almost 100 years. That makes galvanization truly durable.
i. There may be various other ways of corrosion protection; however galvanized coating is one of the most durable forms of corrosion protection. In an ideal condition i.e., without any operation loads on the steel structure i.e., if the galvanized steel is kept, with average coating thickness of 85 microns, it will protect the base material for almost 100 years. That makes galvanization truly durable.
Hot dipped galvanization is a proven and well-established method. HDG members come with guarantee of service life; however, Pre-galvanized steel suppliers do not provide performance guarantee beyond 5 to 10 years. Enough scientific literature is present in case of HDG to demonstrate its performance advantage over pre-galvanised steel.
ii. Hot-Dipped Galvanization is almost maintenance free. Once it is done, there is no requirement of reapplication or recoating. That makes it more sustainable.
In case of pre galvanized material, after some service life the pre-galvanized material needs replacement and / or maintenance.
iii. Indian solar developers are trying to increase the solar project life to 35-40 years instead of present standard of 25 years, as most of the upcoming solar projects in India will be at C3-C4 corrosion zones. It is important to design the BOP systems for 40-50 years as well. Galvanization is a techno – economical, cost effective solution when compared with grit blasted equivalent painting system. PU or alike painting systems must be applied in multiple layers over grit blasted steel surfaces. Usually painting scheme shall have 275 to 325micron thickness as per manufacturer prescription.
However, this cost effectiveness is achievable in HDG only. Corresponding thickness of galvanization compared to 325micron painting is 60 to 80 microns. These 60 to 80 microns of galvanization thickness provide minimum 25 to 30 years of life expectancy under worst condition like corrosion condition greater than C4.
Pre galvanized material does not provide the requisite thickness of galvanization and service life guarantee comparable with HDG and painting system.
iv. Hot-Dipped Galvanizing ensures complete coverage over steel surface, irrespective of its shape and geometry. As a process point of view, in case of hot dipped galvanization, once the structural member is completely fabricated including welding, punching, drilling, cutting etc, it is immersed into molten zinc and kept for requisite time duration. This ensures complete zinc coverage.
However, in case of pre galvanized steel members, this is not possible. The steel members which are fabricated using pre galvanized remain susceptible to corrosion. In manufacturing process of the pre-galvanized sheet (or similar products), a bare steel plate of thickness is passed galvanization process. As a result, zinc coating is applied (of 20/30micron) only on the exposed surfaces. While fabricating the structural member to requisite shape and size it is subjected to welding, punching, drilling, cutting i.e., this work exposes and damages the existing pre galvanized layer., compromising the life of the structure.
v. Hot-Dipped Galvanizations provide superior abrasion resistance. In hot dip galvanization process, the zinc coating is firmly bonded metallurgically to the steel surface. Due to its unique metallurgical bond, a galvanized coating is incredibly tough, offering exceptional performance through all kind of abrasion and shocks.
An initial outer layer of galvanization provides reliability by acting as a buffer zone, helping to absorb any type of initial shock, impacts, abrasions etc. to the galvanized coating and metal surface. Also, the underlying zinc-iron alloy is harder than steel itself and will further reduce any potential penetration of the coating or the exposure of bare steel. This means that a galvanized coating is highly shock, wear, and tear resistant which is particularly suited to areas of high frequency industrial application. A Hot-Dipped Galvanization coating can also help prevent damage during construction, transport, erection, and the other mechanical activities.
This type of protection is not possible in pre-galvanized steel as the galvanized thickness is itself very thin compared to HDG.
vi. Hot-Dipped Galvanization is a fast activity. Once the steel members are fabricated, it requires just a few minutes of immersion time into molten zinc tank post cleaning of the members to ensure complete protection.
This protection in such a short time is not possible in case of pre galvanized material, as the punched, drilled, cut surfaces remains unprotected or it need special treatment in case of special requirements.
vii. Typically, in pre-galvanized material, the claimed 80-micron thickness of galvanization represents 40micron on inner face + 40 micron on outer face of steel; however, in HDG 80 microns is the coating thickness on each side.
viii. In the renewable power sector, all the structures which comprise of thin structural members and cost is worked out on basis of weight of the structural members; in such cases owner or project developer leverages benefit of steel weight from Hot-Dipped Galvanized members, this tonnage benefit is not available in pre-gal structures. The strong bond between zinc and the metal makes it possible to optimize the base material thickness.
However, this advantage of weight reduction is not possible in pre galvanized or PosMAC like materials.
4. Points to Ponder
i. As India is accelerating towards its goal of 300 GW solar capacity by 2030 from 58 GW at present, do we need to change our engineering designs for making a long-term & sustainable solution or should we continue focusing on the designs developed by Western countries, for totally different environmental conditions.
ii. Which all components should be innovated to increase the plant life to 50 years & beyond,



























